Introduction
If you’re a car enthusiast or simply want to understand your vehicle better, knowing how an O2 sensor works is essential. An O2 sensor, or oxygen sensor, plays a crucial role in your car’s engine efficiency and emissions. It helps your car monitor the oxygen level in the exhaust and adjust the air-fuel mixture accordingly. Understanding its function can save you money on fuel and reduce harmful emissions. In this article, we will break down what an O2 sensor is, how it works, and provide a step-by-step guide for maintaining it.
What Is an O2 Sensor?
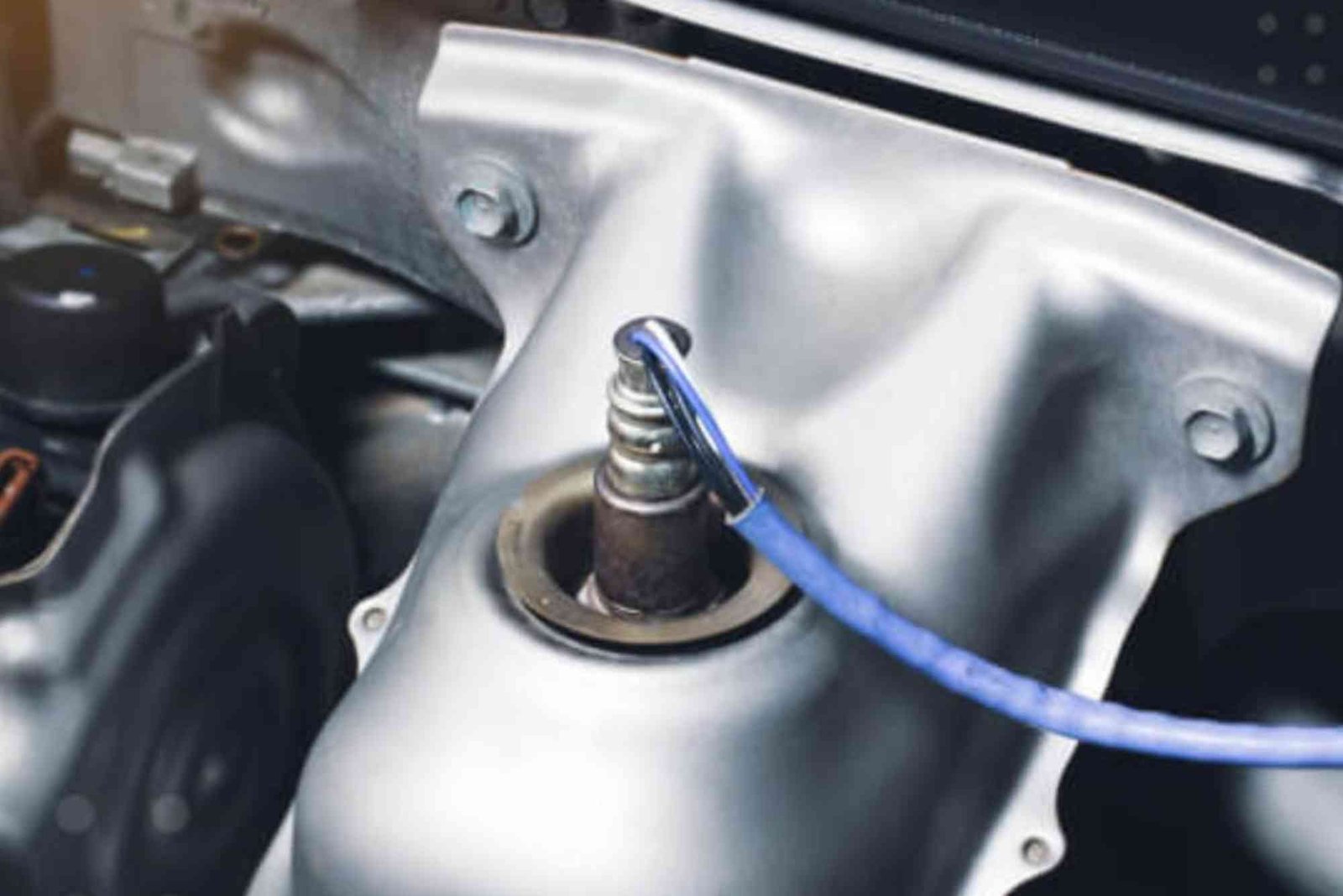
An O2 sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases of a car. It helps the engine’s computer adjust the air-fuel ratio for optimal combustion. Without a properly functioning O2 sensor, your car may run too rich or too lean, affecting performance and fuel efficiency. The sensor is usually located in the exhaust manifold or exhaust pipe.
How the O2 Sensor Works
The O2 sensor generates a voltage based on the oxygen level in the exhaust. A high voltage indicates a rich mixture, while a low voltage signals a lean mixture. The car’s engine control unit (ECU) reads this information and adjusts the fuel injection system to optimize combustion. Modern vehicles may have multiple O2 sensors, including upstream and downstream sensors, to monitor both pre-catalytic and post-catalytic emissions.
Signs of a Faulty O2 Sensor
A malfunctioning O2 sensor can lead to poor fuel economy, engine misfires, rough idling, and increased emissions. The check engine light may illuminate if the sensor fails. Prompt detection and replacement are crucial to maintain vehicle performance and avoid costly repairs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Checking an O2 Sensor
Gather the Necessary Tools
Before checking your O2 sensor, you’ll need basic tools: a digital multimeter, a socket set, and a repair manual specific to your car model. Safety gloves and goggles are also recommended to protect yourself while working near hot engine parts.
Locate the O2 Sensor
Most O2 sensors are installed in the exhaust manifold or exhaust pipe. Upstream sensors are positioned before the catalytic converter, while downstream sensors are placed after it. Consult your car’s repair manual or use an online guide to pinpoint the exact location.
Inspect the Sensor and Wiring
Visually inspect the O2 sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or frayed wiring. Damaged wires can interfere with the sensor’s signal, leading to inaccurate readings. Ensure all connectors are secure and free from rust or dirt.
Test the Sensor with a Multimeter
Set your multimeter to measure voltage. Start the engine and let it reach operating temperature. Carefully measure the voltage output from the sensor. A functioning sensor will typically fluctuate between 0.1 to 0.9 volts as the engine adjusts the air-fuel mixture.
Analyze the Results
If the voltage remains constant or is outside the expected range, the sensor may be faulty. Compare your readings with manufacturer specifications in your repair manual. A failing sensor should be replaced promptly to prevent engine performance issues.
Maintaining Your O2 Sensor
Regular maintenance of your O2 sensor can prolong its lifespan and ensure optimal engine performance. Avoid using leaded fuel, as it can contaminate the sensor. Keep your engine well-tuned, and address any exhaust leaks or misfires promptly. Cleaning the sensor may temporarily improve performance, but replacement is often the most effective solution.
Replacing the O2 Sensor
Replacing an O2 sensor is relatively straightforward. Disconnect the battery, remove the faulty sensor using a socket, and install the new one. Apply anti-seize compound on the threads to ease future removal. After installation, reset the ECU to clear any error codes.
The Importance of O2 Sensors in Modern Cars
O2 sensors are essential for reducing vehicle emissions and improving fuel efficiency. They help cars meet strict environmental regulations and ensure smoother engine performance. Vehicles with multiple sensors can precisely control fuel injection, reducing the likelihood of engine knock or stalling.
If you want to dive deeper into car maintenance, check out our What Is An Tips and What Is An O2 Guide. For more automotive insights, see this Related article on holydubai.com.
Benefits of a Properly Functioning O2 Sensor
A working O2 sensor provides several benefits. Improved fuel economy is one of the most noticeable advantages. Additionally, it reduces harmful emissions, prolongs the life of your catalytic converter, and ensures your car runs smoothly. Ignoring a faulty sensor can lead to expensive repairs and lower overall vehicle efficiency.
Common Questions About O2 Sensors
How Long Does an O2 Sensor Last?
Most O2 sensors last between 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on your vehicle and driving conditions. Regular inspection can help you identify potential failures early.
Can I Drive With a Bad O2 Sensor?
While driving with a faulty O2 sensor is possible, it is not recommended. It can lower fuel efficiency, increase emissions, and potentially damage the catalytic converter.
What Is the Cost of Replacing an O2 Sensor?
The cost varies depending on your car model and sensor type. Generally, replacement costs range from $50 to $250 per sensor, including parts and labor.
How Do I Know If My O2 Sensor Is Bad?
Signs include the check engine light, poor fuel economy, rough idling, or failed emissions tests. Diagnostic tools can confirm the sensor’s status accurately.
Can I Clean an O2 Sensor Instead of Replacing It?
Cleaning can provide a temporary fix, but it is usually not a permanent solution. Sensors degrade over time, and replacement ensures reliable performance.
Understanding what an O2 sensor does and how to maintain it is crucial for car owners. It ensures better fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and smoother engine performance. By following the step-by-step guide above, you can monitor, test, and replace your O2 sensor effectively. Regular maintenance will save money and prevent long-term engine damage.